
Creating Photo-Realistic Engravings
Raster engraving is a simple, yet effective way to design. By using common JPEG images, we will be able to experiment with rastering engraving techniques to create photorealistic engravings. In this lesson, we will focus on using Retina Engrave to import, edit, and run our files. By using this powerful software, we will learn to adjust our image size, engraving styles, laser settings, and more.

Safety First
Before powering on your laser, ensure that your workspace is free of fire, electrical and other safety hazards. Always be aware of all safety precautions when cutting materials with a laser.
Verify that your laser is connected to a computer by using the included ethernet cable.
For any additional setup or troubleshooting, reference your user manual for details
Launch Software
When the boot cycle completes, locate the unique IP address for your machine. For Muse, the wired IP will be listed in the bottom right corner of the touchscreen. To access the wireless IP, go to Settings>Network. For all other machines, use the IP address that appears in the main screen after the boot cycle.
Type this unique number into any web browser. We recommend Google Chrome for best results.

Step 1
Import
Import your designs by selecting the icon below (IMG 1), or by dragging and dropping your file into the workspace. This software detects a wide variety of file types. For this we’re using a simple .JPG photo. The .JPG file format is widely used and can easily be taken from a cell phone photo or found online. We've included the design file, though we encourage you to attempt this with your own .JPG file.

Step 2
Resizing
At this moment, the coloration of the image may look strange, but that will be fixed in the next step. We will begin by resizing the object. Many .jpg images can be very large, so by resizing before other settings, we are able to maximize our working speed by avoiding long processing times.
To resize an object, click on the object to highlight the square adjusters called nodes (IMG 2).
Clicking and dragging these nodes will resize the image, while the top node (IMG 3) will rotate the object.

Step 3
Threshold and Dithering
At this moment, the image is still displayed in a high contrast black and white. The black and white raster feature is great for tracing logos, text, or simple high contrast images that only appear in a single color. Select the image and open the right hand menu by clicking the arrow located in the middle of the browser (IMG 4).

Here, you can adjust the threshold of what’s considered black, and what’s considered white, by using the “B/W Threshold” slider(IMG 5).
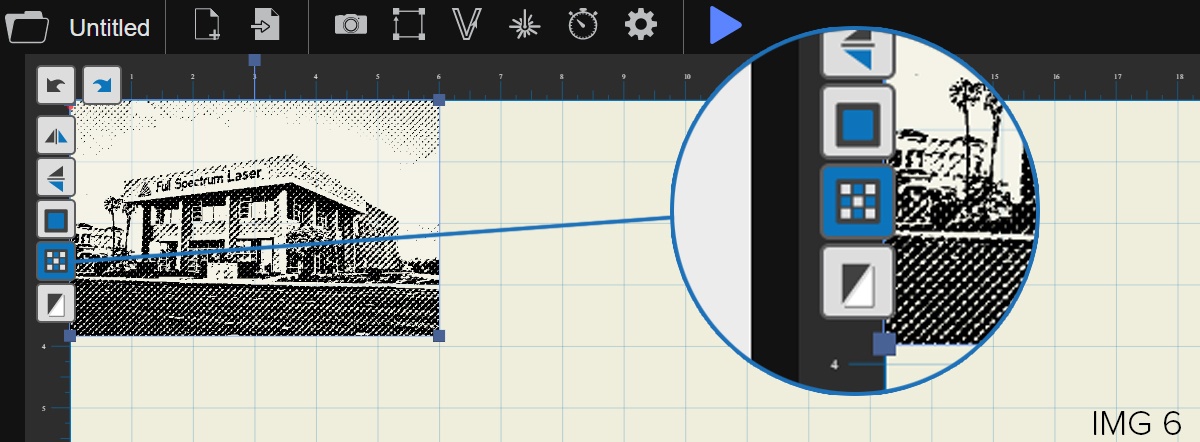
For images that have shadows and depth, like our example image, it’s ideal to use dithering. Dithering creates a series of dots similar to newsprint. This effectively creates a grayscale that is ideal for photorealistic engravings. To dither an object, select the image, and click the dithering button in the menu that appears (IMG 6). Remember that the on screen resolution is intentionally lowered for faster processing. The true resolution of your design will be determined in the next step.

Step 4
Settings
Resolution
In the right hand menu, select the dropdown box to expose the various DPI options (IMG 7). The resolution of your engravings can be controlled by the DPI (Dots Per Inch). DPI options include 250, 500, and 1000. The more dots per inch, the higher precision and quality of your images, while a lower DPI will process and engrave faster. Remember that with a higher DPI (1000), the laser is in contact with the material for a longer period of time and may result in deeper engravings than with a lower DPI (250). Speed and power should be compensated for different DPI settings.

Speed and Power
Next, set your speed and power settings (IMG 8).
Speed and power settings vary on your machine's tube, and your material. It’s recommended to run a test on an inconspicuous part of the material before creating your final piece.
Speed* Power*

Step 5
Focus
Insert your material into the bed and use your focus tool to focus to top of material. For instruction on how to focus your specific machine, reference your user manual.
Step 6
Positioning
There are two positioning modes available to use. You can switch between these by selecting settings (IMG 9)

Then selecting the mode in the dropdown menu that appears(IMG 10). For these first few lessons, we will be using Relative laser positioning.
Relative positioning* Absolute positioning*

By using the directional arrows on the touchscreen or on the software, move the laser dot to the top left corner of your material. (Software)

(Touchscreen)

Step 7
Jog
When the positioning appears in the correct location, press the “Perimeter” icon (IMG 11). Watch the red dot to verify that the piece will fit on your material. Make adjustments if necessary.

Step 8
Run
When the positioning appears correct, close the lid and double-check your cutting checklist. Press the arrow to run your job(IMG 12).

Well Done!
*Speed settings determine how quickly the laser head will move. For faster engravings, 100% is ideal. Lowering the speed will allow you to create deeper engravings as it allows the laser beam to be in contact with the material for a longer period of time.
*Power relates to the output of the laser tube. A 100% power setting will create a deeper engraving while lower settings will create more surface level engravings.
*Relative positioning is relative to the laser head. The red dot from the laser will be considered the top left corner of an image. This makes positioning easier without the use of the Muse camera system.
*Absolute positioning is the default mode and will directly translate the object’s location on the computer workspace to the respective location on the laser bed. Absolute positioning is ideal when using the camera system. We will learn more about the camera feature in lesson 5.
What We Learned
- What is a common file type that can be used for raster engraving?
- .JPG
- In what situations would you use a black and white engraving? Dithered?
- Text, Logos, Single colored images, Line Art
- Photorealistic images or images with grayscale values
- What does DPI stand for?
- Dots Per Inch
- What is the relationship between DPI and the output quality?
- Higher DPI = Higher resolution
- Lower DPI = Lower Resolution
- How do speed and power settings affect the engraving?
- Slower speeds create a deeper engraving, while faster speeds create more shallow engravings
- Higher power settings create deeper engravings, while low power creates more shallow engravings.
Materials: 1/8" Wood
Things to think about:
- What is a common file type that can be used for raster engraving?
- In what situations would you use a black and white engraving? Dithered?
- What does DPI stand for?
- What is the relationship between DPI and the output quality?
- How do speed and power settings affect the engraving?
